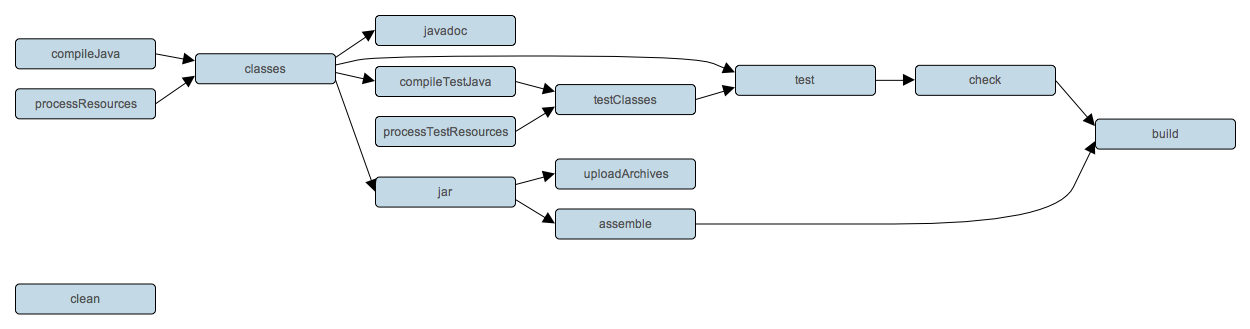
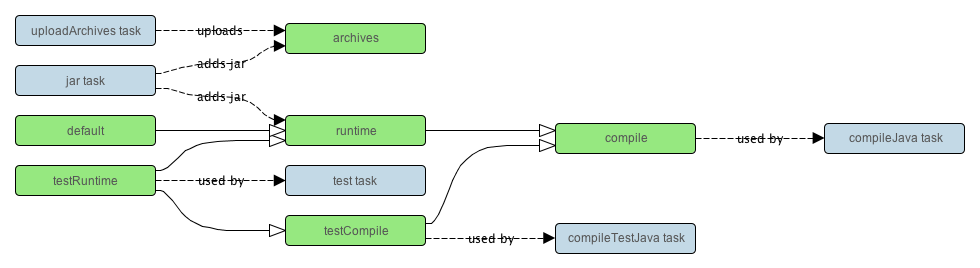
Java 插件向项目添加 Java 编译、测试和捆绑的功能。它是其他许多 Gradle 插件的基础。
The Java plugin adds Java compilation, testing and bundling capabilities to a project. It serves as the basis for many of the other Gradle plugins.
要使用 Java 插件,请在构建脚本中加入以下内容:
To use the Java plugin, include in your build script:
Java 插件引入了一个源集的概念。源集只是一组源文件,它们被一起编译和执行。这些源文件可能包含 Java 源文件和资源文件,有些其他插件可以将 Groovy 和 Scala 源文件包含在源集中。一个源集有一个相关联的编译类路径和运行时类路径。
The Java plugin introduces the concept of a source set. A source set is simply a group of source files which are compiled and executed together. These source files may include Java source files and resource files. Other plugins add the ability to include Groovy and Scala source files in a source set. A source set has an associated compile classpath, and runtime classpath.
源集的一个用途是,将源文件进行逻辑上的分组,以描述它们的目的。例如,你可以使用一个源集来定义一个集成测试套件,也可以使用单独的源集来定义项目的 API 和实现类。
One use for source sets is to group source files into logical groups which describe their purpose. For example, you might use a source set to define an integration test suite, or you might use separate source sets to define the API and implementation classes of your project.
Java 插件定义了两个标准源集,分别是 main 和 test。main 源集包含生产源代码,将其编译并组装到 JAR 文件中。test 源集则包含了单元测试源代码,它们将被编译并使用 JUnit 或 TestNG 来执行。
The Java plugin defines two standard source sets, called main and test. The main source set contains your production source code, which is compiled and assembled into a JAR file. The test source set contains your unit test source code, which is compiled and executed using JUnit or TestNG.
Java 插件向你的项目添加了大量的任务,如下所示。
The Java plugin adds a number of tasks to your project, as shown below.
表 23.1. Java 插件——任务 - Table 23.1. Java plugin - tasks
| 任务名称 Task name |
依赖于 Depends on |
类型 Type |
描述 Description |
CompileJava |
所有产生编译类路径的任务,也包括了 jar 任务,因为项目依赖被包含在 compile 配置中。 All tasks which produce the compile classpath. This includes the jar task for project dependencies included in the compile configuration. |
JavaCompile |
使用 javac 编译 Java 生产源文件。 Compiles production Java source files using javac. |
processResources |
- | Copy |
把生产资源文件复制到生产类目录中。 Copies production resources into the production classes directory. |
classes |
compileJava 和 processResources。有些插件会添加其他的编译任务。 compileJava and processResources. Some plugins add additional compilation tasks. |
Task |
组装生产类目录。 Assembles the production classes directory. |
compileTestJava |
compile 任务,以及所有能产生测试编译类路径的任务。 compile, plus all tasks which produce the test compile classpath. |
JavaCompile |
使用 javac 编译 Java 测试源文件。 Compiles test Java source files using javac. |
processTestResources |
- | Copy |
把测试资源文件拷贝到测试类目录中。 Copies test resources into the test classes directory. |
testClasses |
compileTestJava 和 processTestResources。有些插件会添加其他的测试编译任务。 compileTestJava and processTestResources. Some plugins add additional test compilation tasks. |
Task |
组装测试类目录。 Assembles the test classes directory. |
jar |
compile |
Jar |
组装 JAR 文件 Assembles the JAR file |
javadoc |
compile |
Javadoc |
使用 Javadoc 生成生产的 Java 源代码的API文档 Generates API documentation for the production Java source, using Javadoc |
test |
compile, compileTest,以及所有产生测试运行时类路径的任务。 compile, compileTest, plus all tasks which produce the test runtime classpath. |
Test |
使用 JUnit 或 TestNG 运行单元测试。 Runs the unit tests using JUnit or TestNG. |
uploadArchives |
产生在 archives 中所配置的工件的任务,包括 jar。 The tasks which produce the artifacts in the archives configuration, including jar. |
Upload |
上传在 archives 中所配置的工件,包括 JAR 文件。Uploads the artifacts in the archives configuration, including the JAR file. |
clean |
- | Delete |
删除项目的构建目录。 Deletes the project build directory. |
clean |
- | Delete |
删除指定任务生成的输出文件。例如 cleanJar 将删除由该 jar 任务创建的 JAR 文件,而 cleanTest 将删除由该 test 任务创建的测试结果。 Deletes the output files produced by the specified task. For example cleanJar will delete the JAR file created by the jar task, and cleanTest will delete the test results created by the test task. |
对于你添加到项目中的每一个源集,Java 插件将添加以下的编译任务:
For each source set you add to the project, the Java plugin adds the following compilation tasks:
表 23.2. Java 插件——源集任务 - Table 23.2. Java plugin - source set tasks
| 任务名称 Task name |
依赖于 Depends on |
类型 Type |
描述 Description |
compile |
所有产生源集编译类路径的任务。 All tasks which produce the source set's compile classpath. |
JavaCompile |
使用 javac 编译给定的源集中的 Java 源文件。 Compiles the given source set's Java source files using javac. |
process |
- | Copy |
将给定源集的资源文件复制到类目录中。 Copies the given source set's resources into the classes directory. |
|
compile 和 process。有些插件还为源集添加了其他的编译任务。 compile and process. Some plugins add additional compilation tasks for the source set. |
Task |
组装给定源集的类目录。 Assembles the given source set's classes directory. |
Java 插件还增加了大量构成项目生命周期的任务:
The Java plugin also adds a number of tasks which form a lifecycle for the project:
表 23.3. Java 插件——生命周期任务 - Table 23.3. Java plugin - lifecycle tasks
| 任务名称 Task name |
依赖于 Depends on |
类型 Type |
描述 Description |
assemble |
项目中的所有归档任务,包括 jar。有些插件会向项目添加另外的归档任务。 All archive tasks in the project, including jar. Some plugins add additional archive tasks to the project. |
Task |
组装项目中所有的归档文件。 Assembles all the archives in the project. |
check |
项目中的所有验证任务,包括 test。有些插件会向项目添加另外的验证任务。 All verification tasks in the project, including test. Some plugins add additional verification tasks to the project. |
Task |
执行项目中所有的验证任务。 Performs all verification tasks in the project. |
build |
check 和 assemble check and assemble |
Task |
执行完整的项目构建。 Performs a full build of the project. |
buildNeeded |
build 任务,以及在 testRuntime 配置的所有项目库依赖项的 build 任务。 build and build tasks in all project lib dependencies of the testRuntime configuration. |
Task |
执行项目本身及它所依赖的其他所有项目的完整构建。 Performs a full build of the project and all projects it depends on. |
buildDependents |
build 任务,以及在 testRuntime 配置中对此项目有库依赖的所有项目的 build 任务。 build and build tasks in all projects with a project lib dependency on this project in a testRuntime configuration. |
Task |
执行项目本身及依赖它的其他所有项目的完整构建。 Performs a full build of the project and all projects which depend on it. |
build |
生成 ConfigurationName 配置里的工件的任务。 The tasks which produce the artifacts in configuration ConfigurationName. |
Task |
组装指定配置的工件。该任务由 Base 插件添加,并由 Java 插件隐式应用。 Assembles the artifacts in the specified configuration. The task is added by the Base plugin which is implicitly applied by the Java plugin. |
upload |
上传 ConfigurationName 配置中的工件的任务。 The tasks which uploads the artifacts in configuration ConfigurationName. |
Upload |
以指定的配置组装并上传工件。该任务由 Base 插件添加,并由 Java 插件隐式应用。 Assembles and uploads the artifacts in the specified configuration. The task is added by the Base plugin which is implicitly applied by the Java plugin. |
下图显示了这些任务之间的关系。
The following diagram shows the relationships between these tasks.
Java 插件会假定如下所示的项目布局。这些目录都不需要一定的存在在,或是里面有什么内容。 Java插件不管发现什么都将会进行编译,并处理缺失的任何内容。
The Java plugin assumes the project layout shown below. None of these directories need exist or have anything in them. The Java plugin will compile whatever it finds, and handles anything which is missing.
表 23.4. Java 插件——默认项目布局 - Table 23.4. Java plugin - default project layout
| 目录 Directory |
意义 Meaning |
src/main/java |
Java 生产源代码 Production Java source |
src/main/resources |
生产资源 Production resources |
src/test/java |
Java 测试源代码 Test Java source |
src/test/resources |
测试资源 Test resources |
src/ |
给定源集的 Java 源代码 Java source for the given source set |
src/ |
给定源集的资源 Resources for the given source set |
你可以通过配置适当的源集来配置项目的布局,这点将在下面的章节中详细讨论。以下是一个简单的例子,展示如何改变 main Java 和资源源目录。
You configure the project layout by configuring the appropriate source set. This is discussed in more detail in the following sections. Here is a brief example which changes the main Java and resource source directories.
示例 23.2. 自定义 Java 源代码布局 - Example 23.2. Custom Java source layout
build.gradle
sourceSets {
main {
java {
srcDir 'src/java'
}
resources {
srcDir 'src/resources'
}
}
}
Java 插件向项目添加了一些依赖配置,如下表所示。它将这些配置指定一些任务,如 compileJava 和 test。
The Java plugin adds a number of dependency configurations to your project, as shown below. It assigns those configurations to tasks such as compileJava and test.
表23.5. Java插件 - 依赖配置 - Table 23.5. Java plugin - dependency configurations
| 名称 Name |
继承自 Extends |
在哪些任务中使用 Used by tasks |
意义 Meaning |
| compile | - | CompileJava | 编译时依赖 Compile time dependencies |
| runtime | compile | - | 运行时依赖 Runtime dependencies |
| testCompile | compile | compileTestJava | 用于编译测试代码的其他依赖 Additional dependencies for compiling tests. |
| testRuntime | runtime, testCompile | test | 只用于运行测试的其他依赖 Additional dependencies for running tests only. |
| archives | - | uploadArchives | 由本项目产生的工件(如 jar 包)。 Artifacts (e.g. jars) produced by this project. |
| default | runtime | - | 依赖于本项目的另一个项目所使用的默认配置。包含此项目运行时所需的工件和依赖。 The default configuration used by a project dependency on this project. Contains the artifacts and dependencies required by this project at runtime. |
对于你添加到项目中的每个源集,Java 插件都会添加以下的依赖配置:
For each source set you add to the project, the Java plugins adds the following dependency configurations:
表 23.6. Java 插件——源集依赖配置 - Table 23.6. Java plugin - source set dependency configurations
| 名称 Name |
继承自 Extends |
在哪些任务中使用 Used by tasks |
意义 Meaning |
sourceSetCompile |
- | compileSourceSetJava |
给定源集的编译时依赖 Compile time dependencies for the given source set |
sourceSetRuntime |
sourceSetCompile |
- | 给定源集的运行时依赖 Runtime time dependencies for the given source set |
Java 插件向项目添加了许多约定属性,如下表所示。你可以在构建脚本中使用这些属性,就像它们是 project 对象里的属性一样(见《第 21.3 节,“约定”》)。
The Java plugin adds a number of convention properties to the project, shown below. You can use these properties in your build script as though they were properties of the project object (see Section 21.3, “Conventions”).
表 23.7. Java 插件——目录属性 - Table 23.7. Java plugin - directory properties
| 属性名称 Property name |
类型 Type |
默认值 Default value |
描述 Description |
reportsDirName |
String |
reports |
相对于构建目录,生成报告的目录的名称。 The name of the directory to generate reports into, relative to the build directory. |
reportsDir |
File (只读) File (read-only) |
|
要生成报告的目录。 The directory to generate reports into. |
testResultsDirName |
String |
test-results |
相对于构建目录,生成测试结果.xml 文件的目录名称。 The name of the directory to generate test result .xml files into, relative to the build directory. |
testResultsDir |
File (只读) File (read-only) |
|
生成测试结果.xml 文件的目录。 The directory to generate test result .xml files into. |
testReportDirName |
String |
tests |
相对于报告目录,生成测试报告的目录的名称。 The name of the directory to generate the test report into, relative to the reports directory. |
testReportDir |
File (只读) File (read-only) |
|
生成测试报告的目录。 The directory to generate the test report into. |
libsDirName |
String |
libs |
相对于构建目录,生成库的目录的名称。 The name of the directory to generate libraries into, relative to the build directory. |
libsDir |
File (只读) File (read-only) |
|
要生成库的目录。 The directory to generate libraries into. |
distsDirName |
String |
distributions |
相对于构建目录的目录名称,该目录用于生成分发的文件。 The name of the directory to generate distributions into, relative to the build directory. |
distsDir |
File (只读) File (read-only) |
|
生成分发文件的目录。 The directory to generate distributions into. |
docsDirName |
String |
docs |
相对于构建目录的目录名称,该目录用于生成文档。 The name of the directory to generate documentation into, relative to the build directory. |
docsDir |
File (只读) File (read-only) |
|
用于生成文档的目录。 The directory to generate documentation into. |
dependencyCacheDirName |
String |
dependency-cache |
相对于构建目录的目录名称,该目录用于缓存源代码的依赖信息。 The name of the directory to use to cache source dependency information, relative to the build directory. |
dependencyCacheDir |
File (只读) File (read-only) |
|
用于缓存源代码的依赖信息的目录。 The directory to use to cache source dependency information. |
表 23.8. Java 插件——其他属性 - Table 23.8. Java plugin - other properties
| 属性名称 Property name |
类型 Type |
默认值 Default value |
描述 Description |
sourceSets |
SourceSetContainer (只读)SourceSetContainer (read-only) |
不为 null Not null |
包含项目的源集。 Contains the project's source sets. |
sourceCompatibility |
JavaVersion。也可以使用字符串或数字来设置,如 '1.5' 或 1.5。 JavaVersion. Can also set using a String or a Number, e.g. '1.5' or 1.5. |
当前所使用的 JVM 的值 Value of the current used JVM |
当编译 Java 源代码时所使用的 Java 版本兼容性。 Java version compatibility to use when compiling Java source. |
targetCompatibility |
JavaVersion。也可以使用字符串或数字来设置,如 '1.5' 或 1.5。 JavaVersion. Can also set using a String or Number, e.g. '1.5' or 1.5. |
|
要生成的类的 Java 版本。 Java version to generate classes for. |
archivesBaseName |
String |
|
像 JAR 或 ZIP 文件这样的工件的基本名称。 The basename to use for archives, such as JAR or ZIP files. |
manifest |
Manifest |
一个空的清单 an empty manifest |
包含在所有 JAR 文件中的清单。 The manifest to include in all JAR files. |
这些属性由 JavaPluginConvention 和BasePluginConvention 这些类型的约定对象提供。
These properties are provided by convention objects of type JavaPluginConvention, and BasePluginConvention.
你可以使用 sourceSets 属性访问项目的源集。这是项目源集的容器,它的类型是 SourceSetContainer。除此之外,还有一个 sourceSets{} 脚本块,可以传入一个闭包来配置源集容器。源集容器的使用方式与其他的容器几乎一样,例如 tasks。
You can access the source sets of a project using the sourceSets property. This is a container for the project's source sets, of type SourceSetContainer. There is also a sourceSets { } script block, which you can pass a closure to configure the source set container. The source set container works pretty much the same way as other containers, such as tasks.
示例 23.3. 访问源集 - Example 23.3. Accessing a source set
build.gradle
// Various ways to access the main source set println sourceSets.main.output.classesDir println sourceSets['main'].output.classesDir sourceSets { println main.output.classesDir } sourceSets { main { println output.classesDir } } // Iterate over the source sets sourceSets.all { println name }
要配置一个现有的源集,你只需要使用上面的其中一种访问方法来设置源集的属性。这些属性将在下文中进行介绍。以下是配置main 的 Java 和资源目录的示例:
To configure an existing source set, you simply use one of the above access methods to set the properties of the source set. The properties are described below. Here is an example which configures the main Java and resources directories:
示例 23.4. 配置源集的源代码目录 - Example 23.4. Configuring the source directories of a source set
build.gradle
sourceSets {
main {
java {
srcDir 'src/java'
}
resources {
srcDir 'src/resources'
}
}
}
下表列出了一些重要的源集属性。你可以在 API 文档中找到更多有关 SourceSet 的详细信息。
The following table lists some of the important properties of a source set. You can find more details in the API documentation for SourceSet.
表 23.9. Java 插件——源集属性 - Table 23.9. Java plugin - source set properties
| 属性名称 Property name |
类型 Type |
默认值 Default value |
描述 Description |
name |
String (只读) String (read-only) |
不为 null Not null |
用来确定一个源集的源集名称。 The name of the source set, used to identify it. |
output |
SourceSetOutput (只读) SourceSetOutput (read-only) |
不为 null Not null |
源集的输出文件,包含其编译过的类和资源。 The output files of the source set, containing its compiled classes and resources. |
output.classesDir |
File |
|
生成该源集的类的目录。 The directory to generate the classes of this source set into. |
output.resourcesDir |
File |
|
生成该源集的资源的目录。 The directory to generate the resources of this source set into. |
compileClasspath |
FileCollection |
compile 配置。 compile configuration. |
编译该源集的源文件时使用的类路径。 The classpath to use when compiling the source files of this source set. |
runtimeClasspath |
FileCollection |
output + runtime 配置。 output + runtime configuration. |
执行此源集的类时使用的类路径。 The classpath to use when executing the classes of this source set. |
java |
SourceDirectorySet (只读) SourceDirectorySet (read-only) |
不为 null Not null |
此源集的 Java 源文件。仅包含 Java 源目录中找到的 .java 文件,并排除所有其他文件。 The Java source files of this source set. Contains only .java files found in the Java source directories, and excludes all other files. |
java.srcDirs |
Set<File>。可以使用《第 16.5 节,“指定一组输入文件”》中所讲到的任何一种方法来设置。 Set<File>. Can set using anything described in Section 16.5, “Specifying a set of input files”. |
[ |
该源目录包含了此源集的所有 Java 源文件。 The source directories containing the Java source files of this source set. |
resources |
SourceDirectorySet (只读) SourceDirectorySet (read-only) |
不为 null Not null |
此源集的资源。仅包含资源,并且排除在资源源目录中找到的所有 .java 文件。其他插件(如 Groovy 插件)会从此集合中排除其他类型的文件。 The resources of this source set. Contains only resources, and excludes any .java files found in the resource source directories. Other plugins, such as the Groovy plugin, exclude additional types of files from this collection. |
resources.srcDirs |
Set<File>。可以使用《第 16.5 节,“指定一组输入文件”》中所讲到的任何一种方法来设置。 Set<File>. Can set using anything described in Section 16.5, “Specifying a set of input files”. |
[ |
包含此源集资源的源目录。 The source directories containing the resources of this source set. |
allJava |
SourceDirectorySet (只读) SourceDirectorySet (read-only) |
java |
该源集的所有 .java 文件。有些插件,如Groovy 插件,会将其他 Java 源文件添加到此集合中。 All .java files of this source set. Some plugins, such as the Groovy plugin, add additional Java source files to this collection. |
allSource |
SourceDirectorySet (只读) SourceDirectorySet (read-only) |
resources + java |
该源集的所有源文件,包括所有资源文件和 Java 源文件。有些插件(如 Groovy 插件)会将其他源文件添加到此集合中。 All source files of this source set. This include all resource files and all Java source files. Some plugins, such as the Groovy plugin, add additional source files to this collection. |
要定义一个新的源集,你只需在 sourceSets {} 块引用它。示例如下:
To define a new source set, you simply reference it in the sourceSets { } block. Here's an example:
当你定义一个新的源集时,Java 插件会为该源集添加一些依赖配置,如表 23.6,“Java 插件——源集依赖性配置”所示。你可以使用这些配置来定义源集的编译和运行时依赖。
When you define a new source set, the Java plugin adds some dependency configurations for the source set, as shown in Table 23.6, “Java plugin - source set dependency configurations”. You can use these configurations to define the compile and runtime dependencies of the source set.
示例 23.6. 定义源集依赖 - Example 23.6. Defining source set dependencies
build.gradle
sourceSets {
intTest
}
dependencies {
intTestCompile 'junit:junit:4.11'
intTestRuntime 'org.ow2.asm:asm-all:4.0'
}
Java 插件还添加了大量的任务用于组装源集的类,如表 23.2,“Java 插件——源集任务”所示。例如,对于一个名为 intTest 的源集,你可以通过运行gradle intTestClasses来编译 int 测试类。
The Java plugin also adds a number of tasks which assemble the classes for the source set, as shown in Table 23.2, “Java plugin - source set tasks”. For example, for a source set called intTest, you can run gradle intTestClasses to compile the int test classes.
示例 23.7. 编译源集 - Example 23.7. Compiling a source set
gradle intTestClasses 的输出结果
Output of gradle intTestClasses
> gradle intTestClasses :compileIntTestJava :processIntTestResources :intTestClasses BUILD SUCCESSFUL Total time: 1 secs
添加一个包含源集的类的 JAR 包
Adding a JAR containing the classes of a source set:
示例 23.8. 为一个源集组装一个 JAR 文件 - Example 23.8. Assembling a JAR for a source set
build.gradle
task intTestJar(type: Jar) {
from sourceSets.intTest.output
}
为一个源集生成 Javadoc:
Generating Javadoc for a source set:
示例 23.9. 为一个源集生成 Javadoc: - Example 23.9. Generating the Javadoc for a source set
build.gradle
task intTestJavadoc(type: Javadoc) {
source sourceSets.intTest.allJava
}
添加测试套件以运行源集里的测试
Adding a test suite to run the tests in a source set:
示例 23.10. 运行源集里的测试 - Example 23.10. Running tests in a source set
build.gradle
task intTest(type: Test) {
testClassesDir = sourceSets.intTest.output.classesDir
classpath = sourceSets.intTest.runtimeClasspath
}
Javadoc 任务是 Javadoc 的一个实例。它支持核心 javadoc 的参数选项,以及在 Javadoc 可执行文件的参考文档中描述的标准 doclet 参数选项。对于所支持的 Javadoc 参数选项的完整列表,请参考下面的类的 API 文档: CoreJavadocOptions 和 StandardJavadocDocletOptions。
The javadoc task is an instance of Javadoc. It supports the core javadoc options and the options of the standard doclet described in the reference documentation of the Javadoc executable. For a complete list of supported Javadoc options consult the API documentation of the following classes: CoreJavadocOptions and StandardJavadocDocletOptions.
表 23.10. Java 插件—— Javadoc 属性 - Table 23.10. Java plugin - Javadoc properties
| 任务属性 Task Property |
类型 Type |
默认值 Default Value |
classpath |
FileCollection |
sourceSets.main.output + sourceSets.main.compileClasspath |
source |
FileTree。可以使用《第 16.5 节,“指定一组输入文件”》中所讲到的任何一种方法来设置。FileTree. Can set using anything described in Section 16.5, “Specifying a set of input files”. |
sourceSets.main.allJava |
destinationDir |
File |
|
title |
String |
项目的名称和版本 The name and version of the project |
clean 任务是 Delete 的一个实例。它只是删除由 dir 属性表示的目录。
The clean task is an instance of Delete. It simply removes the directory denoted by its dir property.
表 23.11. Java 插件—— Clean 属性 - Table 23.11. Java plugin - Clean properties
| 任务属性 Task Property |
类型 Type |
默认值 Default Value |
dir |
File |
|
Java 插件使用 Copy 任务进行资源的处理,它为项目中的每个源集添加一个实例。你可以在《第 16.6 节,“复制文件”》找到更多关于复制任务的信息。
The Java plugin uses the Copy task for resource handling. It adds an instance for each source set in the project. You can find out more about the copy task in Section 16.6, “Copying files”.
表 23.12. Java 插件—— ProcessResources 属性 - Table 23.12. Java plugin - ProcessResources properties
| 任务属性 Task Property |
类型 Type |
默认值 Default Value |
srcDirs |
Object。可以使用《第 16.5 节,“指定一组输入文件”》中所讲到的任何一种方法来设置。Object. Can set using anything described in Section 16.5, “Specifying a set of input files”. |
|
destinationDir |
File。可以使用《第 16.1 节,“查找文件”》中所述的任何设置。File. Can set using anything described in Section 16.1, “Locating files”. |
|
Java 插件为项目里的每一个源集添加一个 JavaCompile 实例。一些最常见的配置选项如下所示。
The Java plugin adds a JavaCompile instance for each source set in the project. Some of the most common configuration options are shown below.
表 23.13. Java 插件—— Compile 属性 - Table 23.13. Java plugin - Compile properties
| 任务属性 Task Property |
类型 Type |
默认值 Default Value |
classpath |
FileCollection |
|
source |
FileTree。可以使用《第 16.5 节,“指定一组输入文件”》中所讲到的任何一种方法来设置。FileTree. Can set using anything described in Section 16.5, “Specifying a set of input files”. |
|
destinationDir |
File. |
|
默认情况下,Java 编译器在 Gradle 进程中运行。将 options.fork 设置为 true 将使得在一个单独的进程中进行编译。在Ant javac 任务的情况中,意味着每个编译任务都会 fork 一个新进程,这样就会使编译变慢。相反,Gradle 的直接编译器集成(见上文)将尽可能地重用相同的编译器进程。在这两种情况下,使用 options.forkOptions 指定的所有 fork 选项都将得到重视。
By default, the Java compiler runs in the Gradle process. Setting options.fork to true causes compilation to occur in a separate process. In the case of the Ant javac task, this means that a new process will be forked for each compile task, which can slow down compilation. Conversely, Gradle's direct compiler integration (see above) will reuse the same compiler process as much as possible. In both cases, all fork options specified with options.forkOptions will be honored.
test 任务是 Test 的一个实例。它会自动检测并执行 test 源集中的所有单元测试。测试执行完成后,它还会生成一个报告。它同时支持 JUnit 和 TestNG,可以看一看 test 的完整 API。
The test task is an instance of Test. It automatically detects and executes all unit tests in the test source set. It also generates a report once test execution is complete. JUnit and TestNG are both supported. Have a look at Test for the complete API.
测试在单独的 JVM 进程中执行,与主构建进程隔离。Test 任务的 API 允许你对这种情况进行一些控制。
Tests are executed in a separate JVM, isolated from the main build process. The Test task's API allows you some control over how this happens.
有很多属性可以控制测试进程的启动,包括系统属性、JVM 参数以及要使用的Java 可执行文件。
There are a number of properties which control how the test process is launched. This includes things such as system properties, JVM arguments, and the Java executable to use.
你可以指定是否要并行执行测试。Gradle 通过同时运行多个测试进程来提供并行测试的执行。每个测试进程一次只执行一个测试,所以通常不需要为测试做任何特殊的配置就可以利用这一点。maxParallelForks 属性指定了在给定的任何时间可以运行的最大测试进程数。默认值为1,即不并行执行测试。
You can specify whether or not to execute your tests in parallel. Gradle provides parallel test execution by running multiple test processes concurrently. Each test process executes only a single test at a time, so you generally don't need to do anything special to your tests to take advantage of this. The maxParallelForks property specifies the maximum number of test processes to run at any given time. The default is 1, that is, do not execute the tests in parallel.
测试进程程会将 org.gradle.test.worker 系统属性设置为该测试进程的一个唯一标识符,这个标识符可以用于文件名称或其他资源标识符。
The test process sets the org.gradle.test.worker system property to a unique identifier for that test process, which you can use, for example, in files names or other resource identifiers.
你可以指定在执行了一定数量的测试类之后,重新启动测试进程。这是一个很有用的替代方案,可以让你的测试进程有非常大的堆内存。forkEvery 属性指定了要在测试进程中执行的最大测试类的数量。默认是在每个测试进程中执行的测试数量不限。
You can specify that test processes should be restarted after it has executed a certain number of test classes. This can be a useful alternative to giving your test process a very large heap. The forkEvery property specifies the maximum number of test classes to execute in a test process. The default is to execute an unlimited number of tests in each test process.
该任务有一个 ignoreFailures 属性,用于控制测试失败时的行为。测试任务始终执行它检测到的每个测试,如果 ignoreFailures 值为 false,并且有测试不通过,那它就会停止继续构建。ignoreFailures 的默认值为 false。
The task has an ignoreFailures property to control the behavior when tests fail. Test always executes every test that it detects. It stops the build afterwards if ignoreFailures is false and there are failing tests. The default value of ignoreFailures is false.
testLogging 属性可以配置哪些测试事件需要记录,并且使用什么样的日志级别。默认情况下,对于每个失败的测试都只会打印一个简洁的消息。请参阅 TestLoggingContainer,查看如何把测试日志调整为你的偏好设置。
The testLogging property allows to configure which test events are going to be logged and at which detail level. By default, a concise message will be logged for every failed test. See TestLoggingContainer for how to tune test logging to your preferences.
test 任务提供了一个 Test.getDebug() 属性,可以设置为启动,使 JVM 在执行测试之前等待调试器连接到它的 5005 端口上。
The test task provides a Test.getDebug() property that can be set to launch to make the JVM wait for a debugger to attach to port 5005 before proceeding with test execution.
这也可以在调用时通过 --debug-vm 任务选项进行启用。
This can also be enabled at invocation time via the --debug-jvm task option.
从 Gradle 1.10 开始,可以基于测试名称模式,只包含特定测试。过滤是与测试类包含或排除所不同的一种机制,接下来的段落中将会对其详细介绍(-Dtest.single, test.include 和其他相关的)。后者基于文件,例如测试实现类的物理位置。文件级测试选择不支持的许多有趣的场景,都可以用测试级过滤来实现。其中一些 Gradle 现在就可以处理,而有一些将在未来的版本中得到实现:
Starting with Gradle 1.10, it is possible to include only specific tests, based on the test name pattern. Filtering is a different mechanism than test class inclusion / exclusion that will be described in the next few paragraphs (-Dtest.single, test.include and friends). The latter is based on files, e.g. the physical location of the test implementation class. File-level test selection does not support many interesting scenarios that are possible with test-level filtering. Some of them Gradle handles now and some will be satisfied in the future releases:
- 在指定的测试方法级别上过滤;执行单个测试方法
Filtering at the level of specific test methods; executing a single test method - 基于自定义注解进行过滤(以后实现)
Filtering based on custom annotations (future) - 基于测试层次结构进行过滤;执行所有继承了某一基类的测试(以后实现)
Filtering based on test hierarchy; executing all tests that extend ceratain base class (future) - 基于一些自定义的运行时规则进行过滤,例如某个系统属性或一些静态的特定值(以后实现)
Filtering based on some custom runtime rule, e.g. particular value of a system property or some static state (future)
测试过滤功能具有以下的特征:
Test filtering feature has following characteristic:
- 支持完整的限定类名称或完整的限定方法名称,例如“org.gradle.SomeTest”、“org.gradle.SomeTest.someMethod”
Fully qualified class name or fully qualified method name is supported, e.g. "org.gradle.SomeTest", "org.gradle.SomeTest.someMethod" - 通配符 “*” 支持匹配任何字符
Wildcard '*' is supported for matching any characters - 提供了“--tests”命令行选项,以方便设置测试过滤器。特别适用于传统的“单一测试方法执行”用例。当使用该命令行选项时,构建脚本中声明的包含过滤器将被忽略。
Command line option "--tests" is provided to conveniently set the test filter. Especially useful for the classic 'single test method execution' use case. When the command line option is used, the inclusion filters declared in the build script are ignored. - 鉴于特定测试框架 API 的限制,Gradle 会尽最大努力过滤测试。一些高级的、综合的测试可能不完全符合过滤条件。但是,绝大多数测试和用例都应该能被较好地处理。
Gradle tries best to filter the tests given limitations of particular test framework API. Some advanced, synthetic tests may not be fully compatible with filtering. However, vast majority of tests and use cases should be handled neatly. - 测试过滤取代了基于文件的测试选择。后者可能会在将来被完全取代。我们将会增加测试过滤 API 并添加更多类型的过滤器。
Test filtering supersedes the file-based test selection. The latter may be completely replaced in future. We will grow the the test filtering api and add more kinds of filters.
示例 23.11. 在构建脚本中过滤测试 - Example 23.11. Filtering tests in the build script
build.gradle
test {
filter {
//include specific method in any of the tests
includeTestsMatching "*UiCheck"
//include all tests from package
includeTestsMatching "org.gradle.internal.*"
//include all integration tests
includeTestsMatching "*IntegTest"
}
}
有关更多的详细信息和示例,请参阅 TestFilter 的文档。
For more details and examples please see the TestFilter reference.
使用命令行选项的一些示例:
Some examples of using the command line option:
gradle test --tests org.gradle.SomeTest.someSpecificFeaturegradle test --tests *SomeTest.someSpecificFeaturegradle test --tests *SomeSpecificTestgradle test --tests all.in.specific.package*gradle test --tests *IntegTestgradle test --tests *IntegTest*ui*gradle someTestTask --tests *UiTest someOtherTestTask --tests *WebTest*ui
设置一个 taskName.single = testNamePattern 的系统属性将会只执行匹配指定的 testNamePattern 的测试。该 taskName 可以是完整的多项目路径,如“:sub1:sub2:test”,或者仅是一个任务名称。该 testNamePattern 将被用于形成“**/testNamePattern*.class”的包含模式。如果找不到这种模式的测试,那么将会抛出一个异常。这是为了避免你误认为测试通过。如果执行多个子项目的测试,则该模式将应用于每个子项目。如果找不到特定子项目的测试,则会引发异常。在这种情况下,你可以使用模式的路径标记法,以便模式仅应用于特定子项目的测试任务。或者你可以指定要执行的任务的完整限定名称。你还可以指定多个模式。示例:
Setting a system property of taskName.single = testNamePattern will only execute tests that match the specified testNamePattern. The taskName can be a full multi-project path like ":sub1:sub2:test" or just the task name. The testNamePattern will be used to form an include pattern of "**/testNamePattern*.class". If no tests with this pattern can be found an exception is thrown. This is to shield you from false security. If tests of more than one subproject are executed, the pattern is applied to each subproject. An exception is thrown if no tests can be found for a particular subproject. In such a case you can use the path notation of the pattern, so that the pattern is applied only to the test task of a specific subproject. Alternatively you can specify the fully qualified task name to be executed. You can also specify multiple patterns. Examples:
gradle -Dtest.single=ThisUniquelyNamedTest testgradle -Dtest.single=a/b/ testgradle -DintegTest.single=*IntegrationTest integTestgradle -Dtest.single=:proj1:test:Customer buildgradle -DintegTest.single=c/d/ :proj1:integTest
Test 任务通过检查编译的测试类来检测哪些类是测试类。默认情况下,它会扫描所有 .class 文件。你可以设置自定义包含或排除哪些类,只有这些类才会被扫描。根据所使用的测试框架(JUnit 或 TestNG),会使用不同的标准进行测试类的检测。
The Test task detects which classes are test classes by inspecting the compiled test classes. By default it scans all .class files. You can set custom includes / excludes, only those classes will be scanned. Depending on the test framework used (JUnit / TestNG) the test class detection uses different criteria.
当使用 JUnit 时,我们扫描 JUnit 3 和 4 的测试类。如果符合以下任何标准,则该类将被视为 JUnit 测试类:
When using JUnit, we scan for both JUnit 3 and 4 test classes. If any of the following criteria match, the class is considered to be a JUnit test class:
类或超类继承自
TestCase或GroovyTestCaseClass or a super class extends
TestCaseorGroovyTestCase类或超类使用了
@RunWith注解Class or a super class is annotated with
@RunWith类或超类含有一个带
@Test注解的方法Class or a super class contain a method annotated with
@Test
当使用 TestNG 时,我们扫描带有 @Test 注解的方法。
When using TestNG, we scan for methods annotated with @Test.
请注意,抽象类不会被执行。 Gradle 还将扫描测试类路径中的 jar 文件的继承树。
Note that abstract classes are not executed. Gradle also scan up the inheritance tree into jar files on the test classpath.
如果您不想使用测试类检测,则可以通过设置 scanForTestClasses 为 false 来禁用它。这将使测试任务仅使用包含或排除来查找测试类。如果 scanForTestClasses 被禁用,并且没有指定包含或排除模式,则使用相应的默认值。对于包含的默认值是 “**/*Tests.class”,“**/*Test.class”,而排除的默认值是 “**/Abstract*.class”。
In case you don't want to use the test class detection, you can disable it by setting scanForTestClasses to false. This will make the test task only use the includes / excludes to find test classes. If scanForTestClasses is disabled and no include or exclude patterns are specified, the respective defaults are used. For include this is "**/*Tests.class", "**/*Test.class" and the for exclude it is "**/Abstract*.class".
JUnit 和 TestNG 支持复杂的测试方法分组。
JUnit and TestNG allows sophisticated groupings of test methods.
为对 JUnit 的测试类和方法进行分组,JUnit 4.8 引入了类别的概念。 [9]test 任务允许指定要包含和排除的 JUnit 类别。
For grouping JUnit test classes and methods JUnit 4.8 introduces the concept of categories. [9] The test task allows the specification of the JUnit categories you want to include and exclude.
示例 23.12. JUnit 类别 - Example 23.12. JUnit Categories
build.gradle
test {
useJUnit {
includeCategories 'org.gradle.junit.CategoryA'
excludeCategories 'org.gradle.junit.CategoryB'
}
}
TestNG 框架则有一个非常相似的概念。在 TestNG 中,你可以指定不同的测试组。 [10]你可以在测试任务中配置应该包含在测试执行中或从测试执行中排除的测试组。
The TestNG framework has a quite similar concept. In TestNG you can specify different test groups. [10] The test groups that should be included or excluded from the test execution can be configured in the test task.
示例 23.13. 对 TestNG 测试分组 - Example 23.13. Grouping TestNG tests
build.gradle
test {
useTestNG {
excludeGroups 'integrationTests'
includeGroups 'unitTests'
}
}
test 任务默认情况下会生成以下结果。
The Test task generates the following results by default.
一个 HTML 测试报告。
An HTML test report.
与 Ant Junit report 任务兼容的 XML 格式的结果。许多工具都支持这一格式,比如 CI 服务器。
The results in an XML format that is compatible with the Ant JUnit report task. This format is supported by many other tools, such as CI servers.
有效的二进制格式的结果。该任务从这些二进制结果生成其他结果。
Results in an efficient binary format. The task generates the other results from these binary results.
还有一个独立的 TestReport 任务类型,它可以从一个或多个 Test 任务实例生成的二进制结果中生成 HTML 测试报告。要使用此任务类型,你需要定义一个 destinationDir 以及要包含在报告的测试结果。下面是一个从子项目的单元测试中生成一个组合报告的示例:
There is also a stand-alone TestReport task type which can generate the HTML test report from the binary results generated by one or more Test task instances. To use this task type, you need to define a destinationDir and the test results to include in the report. Here is a sample which generates a combined report for the unit tests from subprojects:
示例 23.14. 为多个子项目创建一个单元测试报告 - Example 23.14. Creating a unit test report for subprojects
build.gradle
subprojects {
apply plugin: 'java'
// Disable the test report for the individual test task
test {
reports.html.enabled = false
}
}
task testReport(type: TestReport) {
destinationDir = file("$buildDir/reports/allTests")
// Include the results from the `test` task in all subprojects
reportOn subprojects*.test
}
你应该注意的是,TestReport 类型结合了多个测试任务的结果,并需要汇总各个测试类的结果。这意味着如果给定的测试类由多个测试任务执行,那么测试报告将包括该类的执行结果,但很难区分这个类的单独执行和它们的输出。
You should note that the TestReport type combines the results from multiple test tasks and needs to aggregate the results of individual test classes. This means that if a given test class is executed by multiple test tasks, then the test report will include executions of that class, but it can be hard to distinguish individual executions of that class and their output.
TestNG 支持参数化测试方法,允许使用不同的输入多次执行特定的测试方法。 Gradle 会在这个测试方法执行的报告中包含参数值。
TestNG supports parameterizing test methods, allowing a particular test method to be executed multiple times with different inputs. Gradle includes the parameter values in its reporting of the test method execution.
给定一个带有两个参数,名为 aParameterizedTestMethod 的参数化测试方法,它将使用这个名称进行报告 :aParameterizedTestMethod(toStringValueOfParam1, toStringValueOfParam2)。这使得在特定的迭代中,很容易识别参数值。
Given a parameterized test method named aParameterizedTestMethod that takes two parameters, it will be reported with the name: aParameterizedTestMethod(toStringValueOfParam1, toStringValueOfParam2). This makes identifying the parameter values for a particular iteration easy.
表 23.14. Java 插件——测试属性 - Table 23.14. Java plugin - test properties
| 任务属性 Task Property |
类型 Type |
默认值 Default Value |
testClassesDir |
File |
sourceSets.test.output.classesDir |
classpath |
FileCollection |
sourceSets.test.runtimeClasspath |
testResultsDir |
File |
testResultsDir |
testReportDir |
File |
testReportDir |
testSrcDirs |
List<File> |
sourceSets.test.java.srcDirs |
jar 任务创建一个包含项目的类文件和资源的 JAR 文件。 JAR文件被声明为在 archives 依赖配置中的一个构件。这意味着这个 JAR 文件在依赖它的项目的类路径中可用。如果将项目上传到仓库中,则这个 JAR 文件会被声明为依赖描述符的一部分。关于如何处理档案,可以在《第 16.8 节,“创建档案”》中了解,而构件配置则可参考《第五十一章,发布构件》。
The jar task creates a JAR file containing the class files and resources of the project. The JAR file is declared as an artifact in the archives dependency configuration. This means that the JAR is available in the classpath of a dependent project. If you upload your project into a repository, this JAR is declared as part of the dependency descriptor. You can learn more about how to work with archives in Section 16.8, “Creating archives” and artifact configurations in Chapter 51, Publishing artifacts.
每个 jar 或 war 对象都有一个 manifest 属性,它是一个单独的 Manifest 属性。当生成档案时,相应的 MANIFEST.MF 文件会被写入存档。
Each jar or war object has a manifest property with a separate instance of Manifest. When the archive is generated, a corresponding MANIFEST.MF file is written into the archive.
示例 7.5. 自定义的 MANIFEST.MF - Example 23.15. Customization of MANIFEST.MF
build.gradle
jar {
manifest {
attributes("Implementation-Title": "Gradle", "Implementation-Version": version)
}
}
你可以创建一个独立的 Manifest 实例。例如,可以用它来在 jar 之间共享清单信息。
You can create stand alone instances of a Manifest. You can use that for example, to share manifest information between jars.
示例 23.16. 创建一个清单对象。 - Example 23.16. Creating a manifest object.
build.gradle
ext.sharedManifest = manifest {
attributes("Implementation-Title": "Gradle", "Implementation-Version": version)
}
task fooJar(type: Jar) {
manifest = project.manifest {
from sharedManifest
}
}
你可以把其他清单合并到任意的一个 Manifest 对象。其他清单可以用文件路径来描述,或者像上面的例子那样,通过引用另一个 Manifest 对象来描述。
You can merge other manifests into any Manifest object. The other manifests might be either described by a file path or, like in the example above, by a reference to another Manifest object.
示例 23.17. 指定档案的单独 MANIFEST.MF - Example 23.17. Separate MANIFEST.MF for a particular archive
build.gradle
task barJar(type: Jar) {
manifest {
attributes key1: 'value1'
from sharedManifest, 'src/config/basemanifest.txt'
from('src/config/javabasemanifest.txt', 'src/config/libbasemanifest.txt') {
eachEntry { details ->
if (details.baseValue != details.mergeValue) {
details.value = baseValue
}
if (details.key == 'foo') {
details.exclude()
}
}
}
}
}
Manifest 会根据在 from 语句中所声明的顺序进行合并。如果基本的清单和合并清单都定义了同一个键的值,那么默认情况下会采用要合并的清单的值。你可以通过添加 eachEntry 来完全自定义结果清单的每一个实体的合并行为,它让你可以访问 ManifestMergeDetails 实例。合并不会立即由 from 语句触发。它是惰性执行的,在生成 jar 或者是通过调用 writeTo 或 effectiveManifest 的时候完成。
Manifest are merged in the order they are declared by the from statement. If the based manifest and the merged manifest both define values for the same key, the merged manifest wins by default. You can fully customize the merge behavior by adding eachEntry actions in which you have access to a ManifestMergeDetails instance for each entry of the resulting manifest. The merge is not immediately triggered by the from statement. It is done lazily, either when generating the jar, or by calling writeTo or effectiveManifest
你可以很轻松地把一个清单写入磁盘。
You can easily write a manifest to disk.
示例 23.18. 指定档案的单独 MANIFEST.MF - Example 23.18. Separate MANIFEST.MF for a particular archive
build.gradle
jar.manifest.writeTo("$buildDir/mymanifest.mf")
关于如何上传档案,将在《第五十一章,发布构件》中描述。
How to upload your archives is described in Chapter 51, Publishing artifacts.
[9] JUnit wiki 包含了有关如何使用 JUnit 类别的详细说明: https://github.com/junit-team/junit/wiki/Categories。
[9] The JUnit wiki contains a detailed description on how to work with JUnit categories: https://github.com/junit-team/junit/wiki/Categories.
[10] TestNG 文档包含了有关测试组的更多详细信息:http://testng.org/doc/documentation-main.html#test-groups。
[10] The TestNG documentation contains more details about test groups: http://testng.org/doc/documentation-main.html#test-groups.